FRP
FRP
Rethinking What Holds Our Structures Together
Concrete has always relied on steel. But what happens when the very material meant to strengthen it begins to corrode?
That’s the question that led engineers to Fiber Reinforced
Polymer (FRP):
a material designed not just to last, but to outlast.



What Exactly Is FRP?
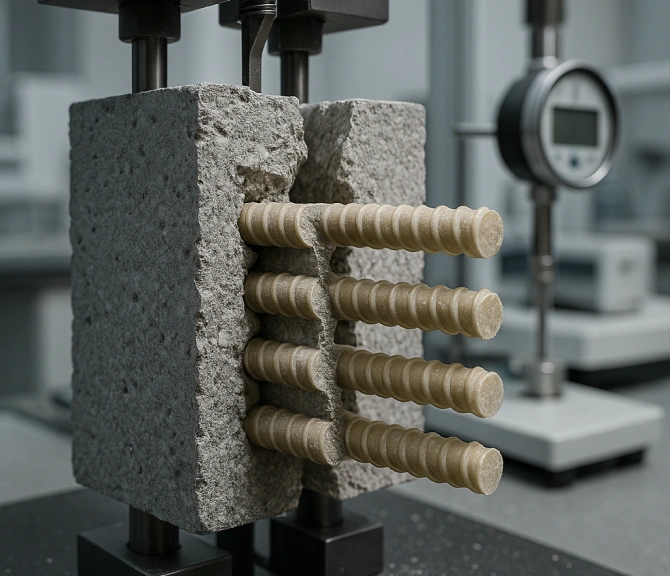
FRP (Fiber Reinforced Polymer) is a composite material made from strong fibers like glass, basalt, or carbon, bonded together with a durable resin.
It’s lightweight, incredibly strong, and completely resistant to corrosion.
‘FRP does everything steel does, except rust.’
Why Engineers Are Moving Beyond Steel
The biggest challenge in concrete structures isn’t design, it’s durability. Water, chemicals, and salt slowly weaken steel, leading to costly repairs and shorter lifespans. FRP changes that equation.
Corrosion-Resistant
FRP doesn’t rust, react with salts, or degrade in harsh environments.
Lightweight & High Strength
Up to five times lighter than steel while delivering exceptional tensile capacity.
Unmatched Durability
Maintains structural integrity even in coastal, chemical, or high-moisture zones.
Versatile Applications
Suitable for bridges, roads, buildings, tunnels, and marine structures.
Sustainability
Longer service life means less repair, less waste, and lower overall carbon impact.
Non-Magnetic & Non-Conductive
Safe for sensitive environments like labs and hospitals.
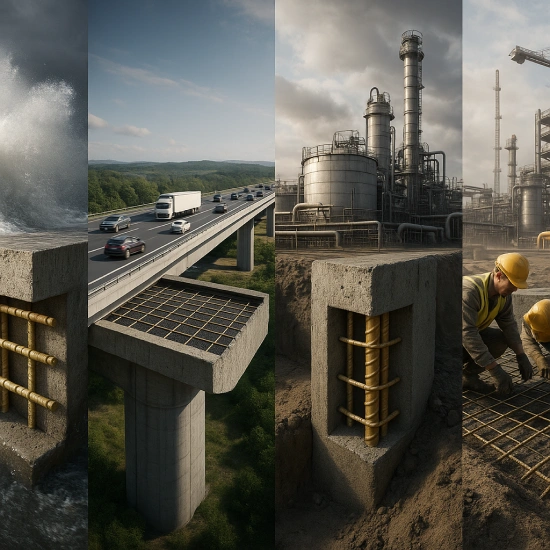

Designed for Where It Matters Most
FRP reinforcement is transforming structures that face extreme conditions:
- Coastal & Marine Projects
- Bridges & Infrastructure
- Industrial Facilities
- Buildings & Foundations
Steel Rebar vs Composite FRP bar
| CHARACTERISTICS |
Metallic
reinforcement class A-III (A400C) |
FRP reinforcement
TAPASHRI ENGINEERING |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Steel | Fibreglass, soaked in a polymer based on epoxy resin |
| Ultimate tensile strength, MPa | 390 | 1100 |
| Modulus of elasticity, MPa | 2,00,000 | 50,000 |
| Elongation, % | 25 | 2.2 |
| Corrosion resistance to aggressive media | Subject to Corrosion | Not Subject to Corrosion |
| Heat Conduction | Is a heat - conduction | Is a not heat - conduction |
| Electro conductivity | Conducts electricity | Non Conducting is a dielectric |
| Minimum Operating temp, C | -40 | -100 |
| Maximum Operating temp, C | +350 | +100 |
| Ultimate Shear strength, MPa | Not rated | 150 |
| Ultimate Compression Strength, MPa | 350 | 300 |
| Strength of adhesion to concrete, MPa | Not rated | 12 |
| Yield strength, N/mm2 | 390 | Not rated |
| Seismic resistance | Depends on the correct selection of reinforcement | Depends on the correct selection of reinforcement |
| Produced profiles, mm | 6-80 | 4-40 |
| Length | The rods of length 6-12 m | According to Customer request |
| Environmentally friendly | Is environmentally friendly | Is not toxic, the degree of impact on humans the environment belongs to the 4 hazard class (low hazard). |
| Longevity | In accordance with building standards | Predicted life is more than 100 years |
Ready to Reinforce Your Next Project with FRP?
Whether you’re designing a bridge, upgrading industrial flooring, or building near the coast, FRP can change the way you approach reinforcement.
